Source: http://img.dictionary.com/
What causes unsatisfactory urination/voiding in men?
When men reach their twilight years, the most common problem they encounter is passing urine. A number of men experience unsatisfactory urination or weak urine flow. More often than not, this predicament is undisclosed until complications arise.
What is prostate gland swelling?
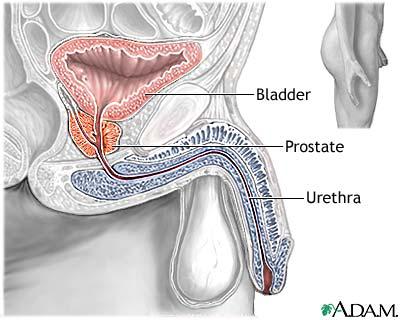
The prostate gland is an organ encircling the proximal end of the male urethra. This gland’s function is to produce the alkaline fluid in men’s semen. A normal prostate gland is about the size of a walnut. However, when men reach the age of 40, stimulations from the hormone testosterone can cause the gland to swell up and constrict the urinary tube (urethra). According to one screening campaign in the National Campaign for Prostate Awareness 2004, more than 50 percent of men screened have symptoms of swollen prostate gland.
What are the signs of prostate swelling?
Often times, patients will have difficulty in passing urine. These signs, among others are:
- Frequenting the toilet, almost every hourly – frequency
- When the urge to use the toilet arrives, the bladder feels like it’s bursting at the seams – urgency
- Nature keeps calling at night – nocturia
- The urine flow takes its own sweet time – poor flow
- The urine keeps dripping towards the end – terminal dribbling
- When it comes to holding the bladder, one cannot hold it well – hesitancy
- Toilet visits are unsatisfactory and one needs to repeat the visits – incomplete voiding
- ‘Blockages’ when passing urine – intermittency
- The urine needs to be pushed out forcefully – straining
What do I do should I have the above symptoms?
A doctor’s confirmation for prostate gland swelling is obtained by getting the details of the patient’s history. By questioning the patient regarding his urinating problems, the doctor will score the patient using the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) chart. The overall score will determine the severity of the illness.
Consequently, a prostate gland examination will be done by the doctors via the anus (digital rectal examination). Through this examination, the firmness of the prostate gland and its surface conditions can be felt. This examination is vital because, if the prostate gland is felt to be hard and its surface bumpy, the doctor should watch out for prostate cancer. Apart from the prostate gland examination, there is one more test that measures the speed of the urine flow whether it is strong or weak. This test is called the uroflow test.
A blood test is done to make sure the kidney function is still intact. Furthermore, a screening test for prostate cancer is also performed.
How is this illness treated?
After the disease is confirmed, the patient will be started on medications. Two categories of medications are available i.e: alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase. The function of alpha-blockers (such as Hytrin, Cardura, Xatral) is to relax the muscles around the prostate so that the urine flow can be improved. Meanwhile, the function of 5-aplha-reductase (such as Avodart and Proscar) is to reduce the testosterone hormone level thus limiting the prostate swelling process. Surgery is only done only when medications fail to treat including other concomitant factors.
What is the long term effect of swollen prostate?
Complications or long term effect of untreated swollen prostate includes:
- Formation of stones inside the urinary bladder.
- Kidney swelling (hydronephrosis) due to prolonged pressure within, exerted from the bladder.
- Recurrent urinary tract infection
- Inguinal hernia, herniation caused by pressure exerted in the pubic region while passing urine.
Dr. Ruhi Fadzlyana is a surgeon, practicing in a hospital in Kuala Lumpur and a lecturer in a local university. This article was translated by Azizul Ismie Mohd Puad from https://www.mmgazette.com/apakah-punca-tidak-puas-kencing-dr-ruhi-fadzlyana/
[This article belongs to The Malaysian Medical Gazette. Any republication (online or offline) without written permission from The Malaysian Medical Gazette is prohibited.]
